.png)
Choosing the right plastic shredder means thinking about material compatibility, shredder type, and key specs. When features match your plastic’s needs, machines like a plastic crusher machine or plastic granulator work better. If someone mismatches a plastic making machine, they risk higher costs, downtime, or even equipment damage.
Key Takeaways
- Identify your plastic type, size, and daily volume to choose a shredder that matches your material’s hardness and shape for better performance and less downtime.
- Select the right shredder type and blade material based on your plastic’s toughness and desired output size to improve shredding efficiency and product quality.
- Check shredder capacity, safety features, and maintenance needs to ensure smooth operation, protect workers, and reduce costly breakdowns.
Identify Your Plastic Material and Shredder Requirements

Determine Plastic Type, Hardness, and Contaminants
Every plastic is different. Some come from factories, while others come from homes or businesses. The source and form of plastic matter because each needs a special shredding approach. Here’s a quick look:
| Category | Description/Examples | Recommended Shredding Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-industrial (clean, dry factory waste) | Shredders for tougher materials; simpler process |
| Post-consumer (used materials with some moisture) | Cutter-compactors to handle moisture and flakes | |
| Shape/Form | Films, fluffy flakes, PE foam, irrigation pipes | Cutter-compactors for delicate, moist materials |
| Raffia, woven/non-woven bags, sacks, hard plastics | Shredders for tougher, bulkier materials |
Hardness also plays a big role. Soft plastics like bags need different blades than hard plastics like thick sheets. For example, carbon steel blades work well for soft plastics, while tool steel or tungsten carbide blades handle very hard plastics. Contaminants such as food, labels, or dirt can clog machines or lower the value of recycled plastic. Clean plastics help the plastic shredder work better and last longer.
Tip: Always check for and remove contaminants like food, labels, or metal before shredding.
Assess Material Size, Shape, and Daily Volume
The size and shape of plastic waste affect which shredder works best. Large, bulky items like pallets or pipes need machines with thick cutters and high power. Small or thin plastics, such as bottles or films, do better with granulators or shredders with more blades for finer cuts.
- Large, thick plastics: Use shear shredders or grinders.
- Thin films or molded parts: Use granulators for uniform flakes.
- Mixed or tough plastics: All-purpose shredders with adjustable settings.
Daily volume matters, too. For example, if a facility processes 8 tons of plastic in 8 hours, it needs a shredder with at least 1.2 tons per hour capacity. Matching the shredder’s throughput to daily needs keeps operations smooth.
Define Desired Output Size and Uniformity
Different recycling processes need different output sizes. Some want small, even flakes, while others need larger pieces. Single-shaft shredders with screens can make precise, uniform particles. Granulators create small, clean flakes for reuse in new products. Four-shaft shredders offer even more control for special jobs.
| Shredder Type | Output Size Control Feature | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Four-shaft shredders | Intermeshing shafts for uniform particles | Rigid plastics, high-security shredding |
| Single-shaft shredders | Sizing screens for precise, uniform sizes | Consistent output needed |
| Granulators | High-speed rotors for small, uniform flakes | Clean feedstock for manufacturing |
Smaller output sizes help with sorting, cleaning, and reusing plastic. The right plastic shredder makes recycling easier and more efficient.
Match Plastic Shredder Type and Performance to Your Needs

Compare Shredder Types: Single Shaft, Double Shaft, Granulators
Choosing the right shredder starts with understanding the main types. Each type works best for certain plastics and tasks. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Shredder Type | Structural Design & Operation | Suitable Materials & Applications | Key Features & Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Shaft Shredder | One rotating shaft with blades cutting against stationary knives | Softer, lighter, uniform materials like plastic film, fiber, waste | Easier maintenance, lower energy use, fine output control |
| Double Shaft Shredder | Two counter-rotating shafts with interlocking blades | Bulky, hard, mixed waste like pipes, drums, e-waste | High torque, handles tough jobs, more complex |
| Granulator | High-speed rotor, slicing action | Sprues, runners, scrap from production lines | Fine granulation, best for size reduction |
Single shaft shredders work well for soft plastics and give more control over output size. Double shaft shredders handle thick, tough, or mixed plastics. Granulators cut plastics into small, uniform pieces, making them perfect for recycling clean scrap.
When working with high-density polyethylene (HDPE), four shaft shredders offer the strongest crushing power and efficiency, especially for tough or large pieces. Double shaft shredders also work well for large output if fine size is not needed.
Select Blade Type, Motor Power, and Safety Features
The right blade makes a big difference. Tough or abrasive plastics need strong blades. Here’s what works best:
| Blade Type / Material | Description / Properties | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Hook Blades | Curved teeth grab and pull materials | Thick pipes, dense sheets |
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Hard, heat-resistant | Hard plastics, high-speed shredding |
| Tool Steel | Tough, resists wear | Hard plastics |
| Alloy Steel | Durable, resists corrosion | General shredding, abrasive plastics |
| Carbide-Tipped Blades | Extremely hard, wear-resistant | Heavy-duty, abrasive materials |
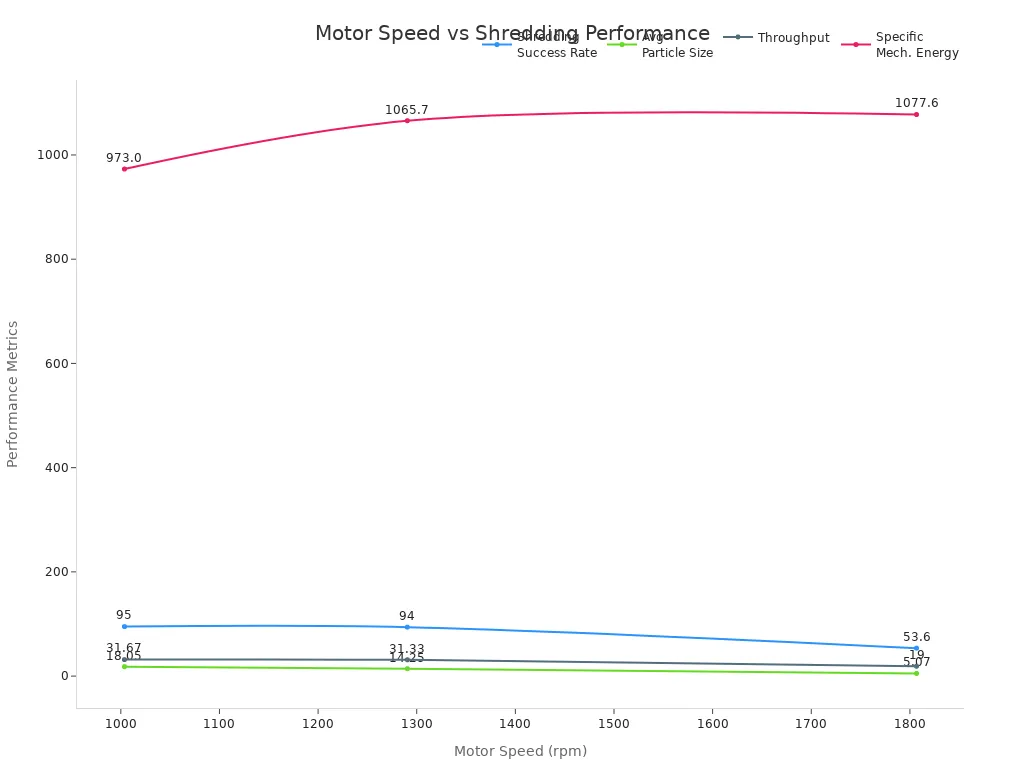
Motor power also matters. More power means the shredder can handle thicker or tougher plastics. For example, a 10 Hp motor at higher speeds shreds plastics faster and into smaller pieces. The chart below shows how motor speed affects shredding results:
Safety features protect workers and equipment. Modern shredders often include:
- Emergency stop buttons
- Safety guards and rails
- Automatic shutdown for jams or overheating
- Fire detection and suppression systems
- Sensors that stop the machine if the feed chamber is open
- Overload and foreign object detection
- Ergonomic designs for easy feeding and maintenance
Tip: Always check for these safety features before buying a plastic shredder.
Evaluate Throughput, Durability, and Maintenance Needs
Throughput tells how much plastic a shredder can process per hour. Double shaft shredders can handle from 30 up to 100,000 kg/h, while single shaft models range from 100 to 9,000 kg/h. Granulators usually process smaller amounts but make finer flakes.
| Shredder Type | Throughput Range (kg/h) | Example Models and Throughput Details |
|---|---|---|
| Single Shaft | 100 – 9,000 | Zibo United Tech: 100 – 1,000 kg/h; WANROOE-TECH: 450 – 1,500 kg/h; Some models up to 9,000 kg/h |
| Double Shaft | 30 – 100,000 | Harden TS series: 3,000 – 15,000 kg/h; ARJES COMPAKTOR 300: 6,000 – 100,000 kg/h; Smaller models: 30 – 135 kg/h |
Durability depends on blade material and machine build. Alloy steel and carbide-tipped blades last longer with tough plastics. Heat treatment and forging make blades stronger and more resistant to wear.
Maintenance needs differ by type. Shredders need regular checks on heavy-duty parts, blade sharpening, and hydraulic systems. Granulators require careful feeding and frequent blade checks to avoid jams. Keeping up with maintenance reduces downtime and keeps the plastic shredder running smoothly.
Common causes of downtime include:
- Feeding problems or blockages
- Overloading or jams
- Poor machine calibration
- Lack of regular maintenance
- Operator errors
To minimize downtime:
- Use automatic feeding systems
- Calibrate machines for the right output size
- Train operators well
- Schedule regular maintenance
Quick Suitability Checklist for Plastic Shredder Selection
Before choosing a plastic shredder, run through this checklist:
- Know your plastics: type, size, and daily volume
- Check machine capacity and throughput
- Look for energy efficiency and easy maintenance
- Review safety features and certifications
- Compare models for technical specs and user feedback
- Plan for operator training and after-sales support
- Consider total cost, including maintenance and energy use
- Ask for live demos or references from other users
Note: Talking to a specialist or manufacturer can help confirm the best fit for your needs.
Choosing the right plastic shredder means checking your material, reviewing the checklist, and asking for expert help if needed. Many users face jamming or blade breakage when they skip compatibility checks:
| Issue | Common Cause |
|---|---|
| Jamming | Overloading, dull blades |
| Blade Breakage | Poor blade quality, misuse |
Regular operator training and safety checks help prevent these problems.
FAQ
How often should someone sharpen shredder blades?
Blades need sharpening every few weeks if used daily. Dull blades slow down work and can cause jams.
Can a plastic shredder handle mixed materials?
Most shredders can process mixed plastics, but metal or glass can damage blades. Always sort out non-plastic items first.
What safety gear should operators wear?
Operators should wear gloves, safety glasses, and ear protection. These items help prevent injuries from sharp plastic pieces or loud noise.
Post time: Jul-30-2025