
The investment for a Plastic Recycling Machine varies significantly. It ranges from tens of thousands to several million dollars. This variation depends on the machine’s capacity, its technology, and its level of automation. The global market for plastic recycling machines shows substantial growth. Experts project this market to reach USD 5.65 billion by 2030. It anticipates a Compound Annual Growth Rate of approximately 7%. This growth highlights increasing demand. Different machine types, such as a Granulator or an Injection Machine Plastic, influence the total cost. A Plastic Injection Moulding Machine or a Plastic Recycle Machine also represents diverse investment levels.
Key Takeaways
- The cost of a plastic recycling machine changes a lot. It depends on its size, how it works, and how much it can do.
- Many things affect the price. These include the machine type, how much plastic it can process, and if it runs by itself.
- New technology makes machines better. This includes smart sorting and washing systems. These can make recycled plastic worth more money.
- Buying a machine is an investment. It helps the environment and can make money over time. This is because recycled plastic is in high demand.
- Governments offer help. They give money or tax breaks to people who invest in plastic recycling. This makes it easier to start.
What Influences the Cost of a Plastic Recycling Machine?

Many factors determine the price of a plastic recycling machine. Understanding these factors helps buyers make informed decisions. The machine’s type, its capacity, and its level of automation all play big roles.
Machine Type and Functionality
The kind of plastic recycling machine directly affects its cost. Different machines perform different tasks. For example, a granulator breaks down plastic into small pieces. An extruder melts plastic and forms new pellets. An injection molding machine creates new products from recycled plastic.
Modern plastic recycling machines typically cost between $10,000 and $200,000. Their specifications and capabilities drive these prices. These include processing capacity, automation level, and quality control systems.
Here are some typical price ranges for various machine types:
- Fully automatic plastic recycling machines: These can range from tens of thousands to millions of yuan for large production lines. Small desktop models cost around tens of thousands of yuan.
- Semi-automatic plastic recycling machines: These generally fall between a few thousand and tens of thousands of yuan. Small crushers might cost 2,000-5,000 yuan. Medium granulators are often 50,000-100,000 yuan.
- Manual plastic recycling machines: These are much cheaper, usually a few hundred to several thousand yuan. Small manual crushers typically cost 500-2,000 yuan.
- Extrusion plastic recycling machines: Small single-screw machines cost 10,000-30,000 yuan. Large twin-screw machines can be 100,000-500,000 yuan or more.
- Injection molding plastic recycling machines: Small machines cost 30,000-80,000 yuan. Medium to large machines are 100,000-300,000 yuan.
- Pyrolysis type plastic recycling machines: These require high investment, often over 500,000 yuan, and can reach tens of millions of yuan. Common equipment costs 500,000-2 million yuan.
- Universal plastic recycling machines: Small machines cost 10,000-50,000 yuan. Medium machines are 50,000-150,000 yuan. Large production lines cost 150,000-500,000 yuan.
- Engineering plastic recycling machines: Small machines cost 30,000-100,000 yuan. Medium machines are 100,000-300,000 yuan. Large equipment can be 300,000-1 million yuan or higher.
The machine’s functionality also impacts its overall cost. Some machines struggle to sort different plastic types. This leads to contamination and lower quality recycled material. This affects the material’s market value. Current machinery may not process complex polymers well. This leaves some plastics unrecyclable. Inability to handle contamination from food or labels also forces discarding recyclable plastics. This increases waste and reduces yield. Some recycling processes use a lot of energy. This leads to higher operational costs. Machinery also has a limited lifespan. It incurs significant maintenance and replacement costs. This creates a financial challenge. New plastic types emerge, and existing machinery may not process them. This requires costly upgrades or new equipment.
However, advanced machinery offers benefits. Investing in state-of-the-art equipment requires significant upfront capital. But machines that produce sellable recycled materials create revenue. This revenue offsets initial and operational costs. Efficient machinery reduces the need for landfill space. This saves money on waste disposal fees. Technological advancements lead to more efficient systems. This lowers operational costs over time.
Processing Capacity and Throughput
The amount of plastic a machine can process per hour is its capacity or throughput. Machines with higher capacity cost more. A small machine might process 100 kilograms per hour. A large industrial machine can process several tons per hour. Higher throughput means the machine handles more material quickly. This requires more robust motors, larger components, and stronger construction. Therefore, a facility needing to process large volumes of plastic will invest more in a higher-capacity plastic recycling machine.
Level of Automation in Plastic Recycling
Automation refers to how much a machine operates without human intervention. A fully automated system costs more upfront than a manual or semi-automatic one. However, automation brings significant long-term benefits. Automated systems reduce the need for many workers. They also minimize errors in waste processing.
For example, Emmet County Recycling facility used an AI-powered system. This helped them create a more stable workforce. They hired fewer, higher-paid employees. Former temporary workers became full-time with benefits. A facility in California, ACI, integrated automation technology. They achieved a 59% reduction in labor costs. They recovered their investment within three months. Recycling robots contribute to long-term savings. They reduce labor costs and minimize processing errors. This makes the initial investment worthwhile over time.
Technology and Innovation in Recycling Machines
New technologies significantly impact the cost and efficiency of a Plastic Recycling Machine. Advanced innovations make machines more effective. They also increase their price.
Latest advancements in plastic sorting include:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications:
- Computer Vision Systems: These systems use high-resolution cameras and algorithms. They analyze color, shape, and texture in real-time. Machine learning models constantly improve their recognition.
- Deep Learning Algorithms: These are complex neural networks. They process visual information quickly. They make split-second decisions. They achieve sorting accuracy rates over 95%.
- Spectroscopic Technologies:
- Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy: This non-destructive method uses infrared light. It identifies different plastic types like PET, HDPE, and PVC. It does this based on their unique spectral signatures.
- Hyperspectral Imaging: This combines imaging with spectroscopy. It uses hundreds of spectral bands. This allows for detailed material analysis. It identifies contaminants and small variations.
- Robotic Sorting Solutions:
- AI-Powered Robotic Arms: These arms combine precise mechanics with advanced recognition. They sort at high speeds. They adapt to new packaging designs.
- Smart Gripper Technology: This technology uses sensors and adaptive pressure control. It handles various sizes and shapes gently but securely. It uses tactile feedback to detect material properties.
- Data Analytics and Process Optimization:
- Real-time Monitoring Systems: These systems provide constant feedback. They show sorting performance and equipment efficiency. They analyze data from many sensors.
- Predictive Maintenance: This analyzes performance data. It predicts possible failures. This minimizes downtime. It keeps sorting accuracy consistent.
The latest technological advancements in plastic washing machines include:
- Current Innovations:
- High-Efficiency Wash Systems: These systems reduce water and energy use.
- Integrated Drying Units: These units minimize processing time and waste.
- Automated Sorting: This separates contaminants during washing.
- Smart Monitoring: This uses AI to optimize cleaning cycles and reduce waste.
- Future Developments:
- Closed-Loop Water Systems: These systems recycle and reuse washing water.
- AI Integration: This allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of washing processes.
- Modular Designs: These designs allow for scaling to fit small and large facilities.
Chemical recycling technologies are generally more expensive than mechanical recycling. This cost difference is clear in the current stage of chemical recycling development.
Manufacturer and Brand Reputation
The manufacturer and brand reputation also influence the cost of a plastic recycling machine. Well-known brands often charge more. They have a reputation for reliability and durability. Lesser-known brands typically sell their equipment at lower prices.
Leading manufacturers like Caterpillar, John Deere, Komatsu, and Volvo usually have higher prices. They have a strong reputation for quality, durability, and customer support. Established brands offer superior reliability, advanced technology, and excellent after-sales service. This contributes to their higher pricing. High-end brands set higher prices because they serve premium markets. Customers in these markets prioritize performance and long-term reliability. For example, a Caterpillar excavator might cost more than a lesser-known brand with similar features. This is mainly due to Caterpillar’s strong brand reputation. It guarantees long-term support and better resale value.
Initial Investment Versus Long-Term Value of a Plastic Recycling Machine
The initial purchase price of a plastic recycling machine is only one part of the total cost. Businesses must also consider the long-term operational expenses and potential revenue. These factors determine the true value of the investment.
Operational Costs and Energy Efficiency
Operational costs significantly impact the long-term profitability of a plastic recycling operation. Energy consumption is a major component of these costs. Modern equipment features better insulation and improved temperature control. This leads to optimized heating and cooling cycles. These cycles waste less energy. New facilities use maximized heating and cooling systems. This minimizes power use with every production cycle. Closed-loop cooling systems reuse water. This substantially reduces water consumption and increases energy efficiency.
Modern plastic recycling plants incorporate energy-efficient systems. These systems minimize operational costs and maximize throughput. Energy-efficient components and optimized processing cycles contribute to lower operational costs. They also improve the return on investment. An innovative energy-efficient operating system significantly reduces power consumption. It maintains high processing capacity. Smart power management features automatically adjust energy usage. This minimizes waste based on processing load. Regenerative drives recover energy from braking mechanisms. They redirect it back into operation. Advanced thermal management systems optimize heating and cooling cycles. This reduces energy requirements. Variable frequency drives ensure optimal power consumption across different operational states. Detailed consumption analytics from the energy management system enable further efficiency improvements. These comprehensive approaches typically result in 30-40% lower power consumption compared to conventional systems.
Maintenance and Spare Parts for Recycling Equipment
Maintaining a plastic recycling machine requires ongoing investment. This includes regular service and replacing worn parts. An initial spare parts inventory can cost between $15,000 and $60,000. Replacement wear parts typically cost $0.008 to $0.015 per kilogram processed annually. Wear parts, such as blades, screens, and seals, are usually excluded from standard warranties. Businesses should maintain an adequate inventory of critical wear items and backup components. This includes spare granulator blades, screens, and motors.
Access to reliable spare parts and service support is vital. It helps maintain the machine’s performance. Using genuine parts and authorized service technicians ensures the machine operates at its best. It also maintains warranty coverage. Aftermarket parts may seem cheaper at first. However, they often lead to higher costs. This happens through reduced performance, increased wear, and potential damage to other components.
Potential Revenue from Recycled Materials
A plastic recycling machine generates revenue by producing sellable recycled materials. The market value of these materials depends on several factors, especially purity.
| Material Type | September US-wide Average Price Change (Month-on-Month) | September US-wide Average Price Change (Year-on-Year) |
|---|---|---|
| Post-consumer recycled PET flake (for packaging) | Down 7% | Down 3% |
| Post-consumer, food grade RPET pellet | Down 5% | Down 12% |
| Post-consumer, natural recycled HDPE pellet (food-grade and non-food grade) | Down 11% | Up 21% |
| Post-consumer, mixed colored RHDPE pellet | Flat | N/A |
| Material Type | Location | Quarter | Average Price (USD/metric ton) | Price Change (Quarter-on-Quarter) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-PET Food Grade Pellets | U.S. | Q2 2025 | 1672 | Up 3.5% |
| Post-consumer PET Bottle Bales (Premium-grade) | Los Angeles, USA | Q1 2025 | 577 | Up 0.8% |
| Flakes | Los Angeles, USA | Q1 2025 | N/A | Slipped slightly |
| Food Grade Pellets | Los Angeles, USA | Q1 2025 | 1615 | Up 0.6% |
| Post-consumer PET Bottle Bales | Hamburg, Europe | Q1 2025 | 571 | Down 2.4% |
| Food Grade Pellets | Hamburg, Europe | Q1 2025 | 1657 | Down 1.3% |
| Flakes | Hamburg, Europe | Q1 2025 | N/A | Slipped 1.6% |
| Flakes | Jeddah, Saudi Arabia | Q1 2025 | 791 | Down 0.2% |
| Flakes | Shanghai, China | Q1 2025 | 825 | Down 1.1% |
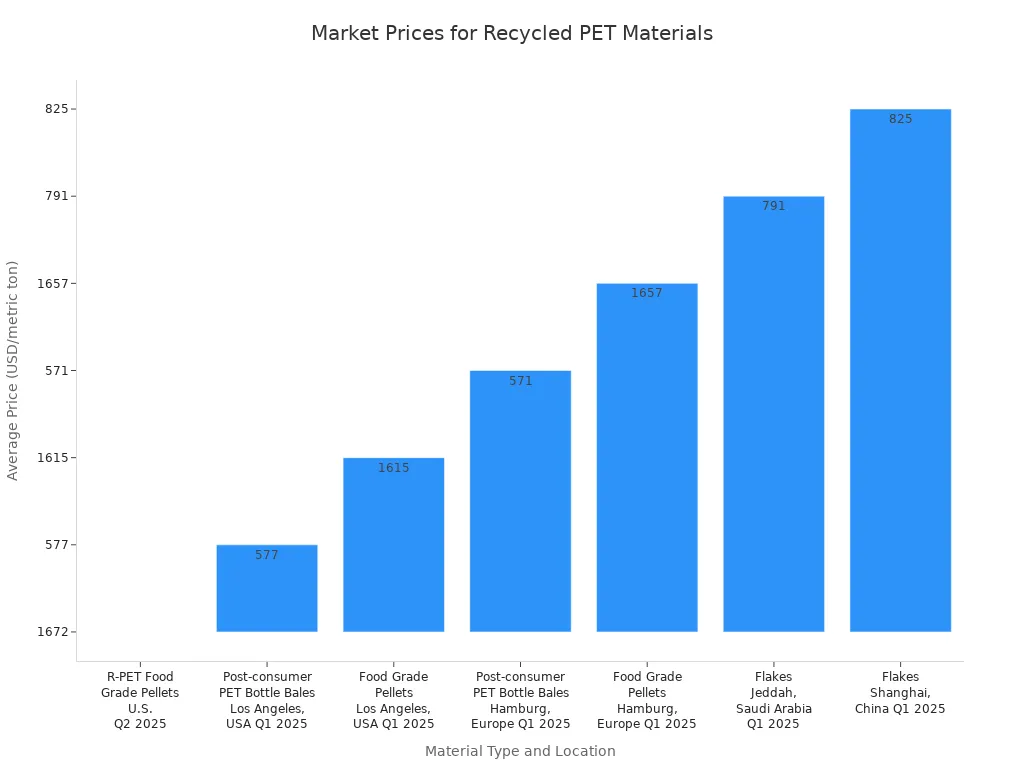
Contamination significantly impacts the value of recycled plastic. A contamination rate as low as 5% can drastically reduce the value of a recycled plastic bale by 40% to 60%. It can even make it unusable for high-value applications. Advanced sorting technology, such as NIR sorters, can elevate the purity rate of plastic streams from a typical 85% to over 98%. This substantial increase in purity can boost the material’s value by 30-50%. It transforms standard-grade plastic pellets into premium, often food-grade, products. This opens new markets. Advanced washing and decontamination, like a hot-wash system, can increase the price of rPET flakes by $100-$200 per ton. Clear rPET flakes can command a 15-20% higher price than mixed-color flakes. High-quality, food-grade rPET pellets sell for $1,400 to $1,900 per ton. This often provides a competitive price advantage compared to virgin PET.
Government Incentives and Subsidies for Plastic Recycling
Governments worldwide recognize the critical role of plastic recycling. They often provide various incentives and subsidies. These programs encourage businesses and municipalities to invest in recycling infrastructure. Such support helps offset the initial high costs of equipment and operations. It makes recycling projects more financially attractive.
In the United States, the bipartisan CIRCLE Act proposes a significant incentive. This act offers a 30% investment tax credit for recycling infrastructure. This credit aims to modernize recycling systems. It also strengthens domestic supply chains. The act supports the American economy by creating jobs. It returns materials to domestic markets. This tax credit will phase out over 10 years. Local municipalities investing in waste reduction will receive a direct rebate. The CIRCLE Act encourages investment in the domestic recycling economy. It rewards businesses and communities. They invest in American recycling infrastructure. This accelerates investment. It also reduces the financial burden on governments.
These government programs play a crucial role. They reduce financial barriers for new and expanding recycling operations. They help improve the overall economic viability of plastic recycling. This support ensures a more sustainable future. It also contributes to a circular economy.
Investment Scales for a Plastic Recycling Machine

The investment required for a Plastic Recycling Machine varies greatly. It depends on the scale of the operation. Businesses can choose from small, medium, or large-scale systems. Each scale meets different needs and budgets.
Small-Scale Plastic Recycling Machines
Small-scale plastic recycling machines are ideal for community projects or pilot programs. These systems offer a lower entry cost. Estimates place the equipment cost for a small-scale plastic recycling plant between $50,000 and $200,000. These machines typically process smaller volumes of plastic. They help local initiatives manage waste. They also produce recycled materials for local use.
Medium-Scale Industrial Plastic Recycling Units
Medium-scale industrial plastic recycling units serve a broader range of businesses. These mid-range industrial systems typically process more material. Their output capacity ranges from 300 to 800 kg/hour. Many industries use these units.
- Plastic manufacturers and molders recycle in-house production waste. This includes sprues, defective parts, or trimmings. They reduce material costs and waste.
- Recycling companies convert post-consumer plastic waste. This includes bottles, bags, and packaging films. They turn it into resin pellets for sale to manufacturers. These pellets become feedstock for new products. Examples include bottles, containers, plastic lumber, pipes, and textile fibers.
- Compounding and material development companies mix recycled plastics with additives. They create materials with specific properties for niche industries. These include automotive parts and construction materials.
Plastic granulators are key parts of these units. They support recycling, reprocessing, and production in several industries: - Injection molding plants reuse sprues, runners, and defective molded parts.
- Blow molding units recycle bottles, drums, and hollow containers.
- Extrusion units recover trimmings and off-spec profiles or sheets.
- Plastic dana making units generate granules for pelletizing.
- Plastic recycling plants convert post-consumer plastic into secondary raw materials.
- The packaging industry reprocesses film scraps, bubble wrap, and sheet waste.
Large Industrial Plastic Recycling Facilities
Large industrial plastic recycling facilities require significant capital. These facilities handle massive volumes of plastic waste. The capital expenditure (CAPEX) for establishing such a facility can range from $5 million for a smaller, basic setup to over $30 million for a large, highly automated plant. This initial investment covers several key areas:
- Land acquisition
- Machinery
- Infrastructure
Specialized equipment, like optical sorters and balers, typically accounts for 60-70% of this initial investment. Total project costs can also range from $5 million to over $30 million. The scale and technology employed determine the final cost.
Understanding the Return on Investment for a Plastic Recycling Machine
Investing in a plastic recycling operation involves more than just the initial purchase price. Businesses must also consider the long-term benefits and financial returns. These factors help determine the true value of the investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Benefits
Plastic recycling offers significant environmental advantages. It reduces the need for new raw materials. It also lowers energy consumption and decreases pollution. Using recycled plastic dramatically cuts down on greenhouse gas emissions.
| Metric | CO2e per tonne |
|---|---|
| Virgin plastic production | 2,383 kg |
| Closed-loop plastic recycling | 202 kg |
| Reduction from recycling | 2,181 kg |
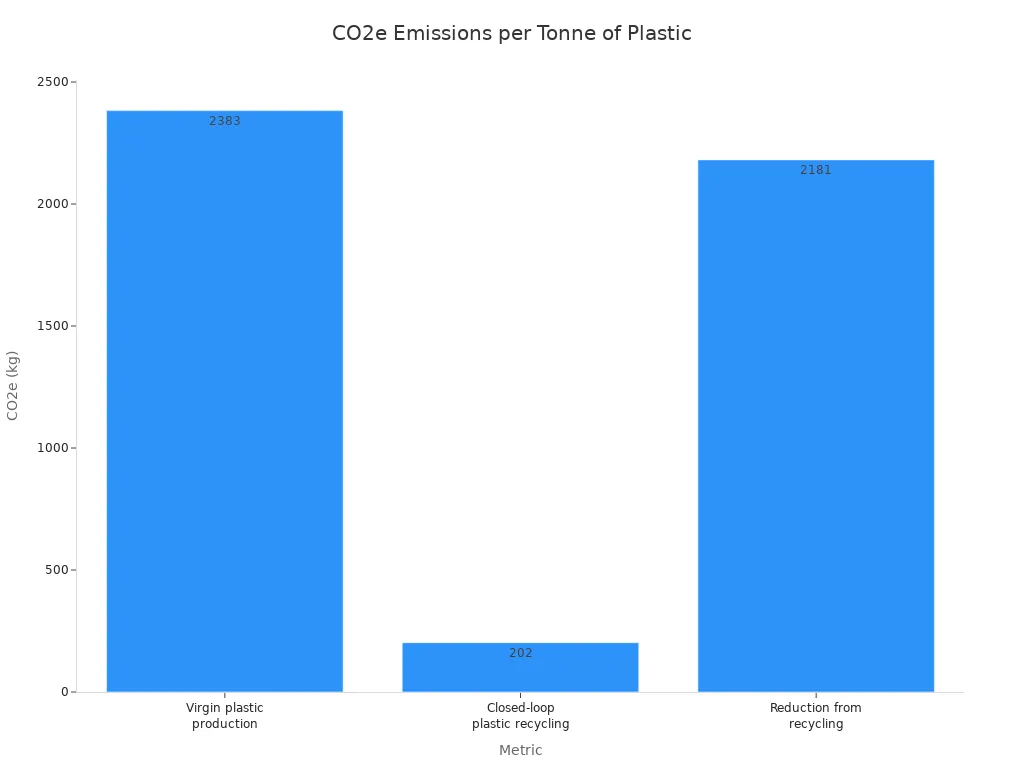
Using recycled plastic results in an emissions footprint over 10 times lower than using virgin plastic. This significant reduction happens because recycling plastic requires much less energy. It leads to at least a 50% lower carbon footprint for recycled plastic.
Globally, people have produced over 9200 million metric tonnes (Mt) of plastic. A large part, 6900 Mt, has not been recycled. It has accumulated in landfills or spread into the environment. This represents a huge missed economic chance and causes environmental harm. Recycling offers a way to handle the growing global plastic waste problem. It provides an alternative to landfills, which have limited space and risk leaking toxic chemicals. It also offers an alternative to waste-to-energy incineration, which can release hazardous chemicals and gases. Embracing plastic recycling can generate substantial profits. These profits could reach up to USD$60 billion by 2030 within the petrochemicals and plastics sector.
Economic Viability and Payback Period
Assessing the economic viability of a plastic recycling project involves looking at several financial metrics. These metrics help determine if the investment will be profitable.
- Import Prices: Businesses use these prices to analyze the cost of plastic waste imports.
- Recycling Costs: This includes several parts:
- Labor: Calculated by multiplying labor input intensity by hourly earnings.
- Electricity: Derived by multiplying per-unit electricity consumption by industrial electricity prices.
- Rent: Based on the area needed for recycling per kilogram of plastic waste, multiplied by annual industrial rent.
- Value of Recycled Plastics (Product Price): The unit price of recycled plastics determines this value. It often compares to primary plastics.
- Physical Loss during Mechanical Recycling Process: This is not a direct financial metric. However, it greatly affects the amount of sellable recycled material. This impacts revenue and overall financial viability.
- Required Recycling Rate (RRR): This defines the economic break-even point. At this point, revenue from recycling matches the total costs (imports and recycling process).
The average payback period for a medium-scale plastic recycling machine investment, specifically for HDPE recycling equipment, typically ranges from 18 to 36 months. This duration can change based on factors like the size of the operation, the cost of raw materials, and the value of the final recycled products. Larger industrial systems often achieve quicker returns. They benefit from economies of scale.
Market Demand for Recycled Plastics
The market for recycled plastics is growing rapidly. This growth shows increasing demand for sustainable solutions across many industries. The recycled plastics market is expected to grow from $69.4 billion in 2023 to $120 billion by 2030. This represents a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.1%.
In 2023, the recycled plastics market was valued at USD 51.7 billion. Experts anticipate a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5% from 2024 to 2030. Polyethylene (PE) was the leading resin. It accounted for over 26% of global revenue. This is largely due to its wide use in packaging. The packaging sector itself held over 37% of the global market share. This happened because of the increasing demand for sustainable containers in food and beverage, personal care, and industrial applications.
| Industry | Share of Total Demand | Key Recycled Plastics Used |
|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Over 40% | rPET, rHDPE |
| Construction & Infrastructure | N/A | Recycled HDPE, LDPE, polypropylene |
| Automotive Industry | N/A | Recycled polymers (for interior components, 3D-printed parts) |
| Fashion & Textiles | N/A | rPET |
| Electronics & Appliances | N/A | Recycled ABS |
| Agriculture | N/A | N/A |
Regulations and corporate sustainability goals also drive the demand for recycled plastic materials.
- The EU’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) mandates the use of recycled content. It also promotes packaging design for recyclability. This directly increases demand for high-quality recyclate.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Schemes make producers financially responsible for their packaging’s end-of-life. The PPWR harmonizes EPR fee modulation. This means companies pay lower fees for easily recyclable packaging with recycled content. They pay higher fees for difficult-to-recycle packaging. This ‘eco-modulation’ provides a direct financial incentive to use recycled materials.
- Financial Incentives and Penalties mean businesses face significant cumulative costs if their packaging portfolios are not optimized for recyclability. Those who adopt sustainable designs benefit from lower fees and reduced regulatory risk. For example, using a fully recyclable PET bottle with 30% recycled content can lead to fee discounts. Non-recyclable multi-material sachets incur much higher fees.
These regulations lead to several changes in how companies operate:
- Supply Chain Adjustments: Companies must find new suppliers for recycled materials. They also invest in research and development for innovative packaging designs.
- Product Redesign: Packaging formats unable to meet recyclability criteria by 2030 will be phased out. This leads to a return to simpler, single-material packaging.
- Consumer Expectations: Evolving consumer demand for sustainable packaging makes it a key selling point. This encourages companies to adapt quickly. They enhance their brand image as environmentally responsible.
Investing in a Plastic Recycling Machine is a strategic decision for any business. One must carefully consider the initial purchase cost, ongoing operational expenses, and the potential revenue generated from recycled materials. This comprehensive evaluation reveals the true value. The ‘cost’ is not merely an expense. It represents a significant investment in environmental sustainability and long-term profitability. Companies make a forward-thinking choice for a better future.
FAQ
What is the typical cost range for a plastic recycling machine?
The investment for a plastic recycling machine varies greatly. It can range from tens of thousands to several million dollars. This depends on the machine’s capacity, technology, and automation level. Small desktop models cost less, while large industrial lines cost more.
Post time: Oct-24-2025